Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
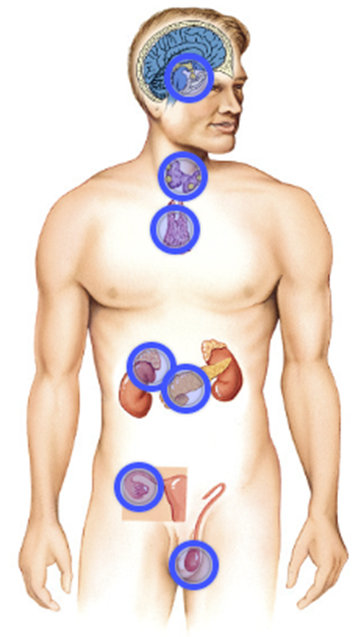
The endocrine system is one of the most important control systems of the human body. It is made up of glands that produce and release hormones. These hormones act as chemical messengers that travel through the blood and regulate various body functions such as:
- Mood and emotions
- Growth and development
- Metabolism (energy use)
- Reproduction
- Response to stress
Without the endocrine system, our body would not be able to maintain balance (homeostasis).
When we think about the human body, most of us picture the heart pumping blood, the brain managing our thoughts, or the lungs helping us breathe. But there is another powerful system working behind the scenes every second: the Endocrine System.
This system doesn’t make noise like a heartbeat or show movement like muscles, but it controls almost every part of our growth, emotions, energy, and health. From how tall we grow to how happy we feel, how hungry we are, and how we handle stress, hormones from the endocrine system are always at work.
In today’s fast-paced world, where stress, lifestyle diseases, and hormonal imbalances are common in India and around the globe, understanding the endocrine system is more important than ever. This blog will provide a complete guide to the endocrine system in simple terms, so that even a school student or someone without a medical background can understand it clearly.
What is the Endocrine System?
The Endocrine System is a group of glands in our body that produce and release hormones. These hormones act as messengers. They travel through the blood and inform different parts of the body about what to do.
For example:
- When you are hungry, your stomach releases hormones that tell your brain it’s time to eat.
- When you are scared, your adrenal glands release adrenaline, making your heart beat faster.
- When you are a teenager, hormones control puberty, making your body change.
Simply put:
👉 The endocrine system is like the WhatsApp of the body – sending quick, important messages between organs so everything works smoothly.
How Hormones Work – The Chemical Messengers
Hormones are special chemicals made by endocrine glands. They enter the bloodstream and travel to target organs.
Example:
- The thyroid gland makes thyroid hormone.
- This hormone travels through blood and reaches cells, telling them how fast to use energy.
Types of hormones:
- Steroid hormones (e.g., cortisol, estrogen, testosterone) – made from fats, usually slow-acting but long-lasting.
- Peptide hormones (e.g., insulin, growth hormone) – made from proteins, work quickly but for shorter periods.
Think of hormones like phone notifications:
- Some are urgent (adrenaline when you’re in danger).
- Some are long-term (growth hormone over years).
The Major Endocrine Glands and Their Functions
🧠 Pituitary Gland – The “Master Gland”
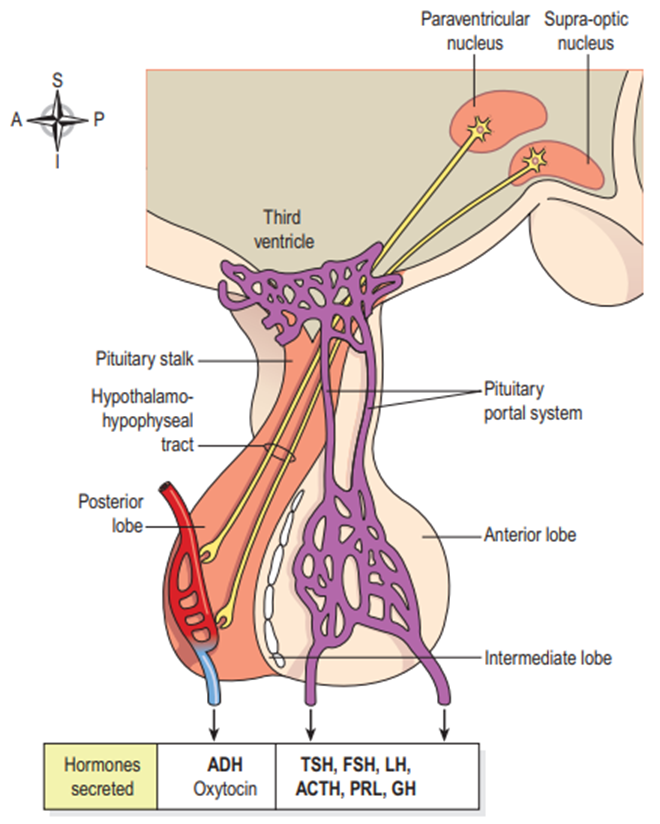
Location: Base of the brain.
Function: Controls almost all other glands.
Hormones: Growth hormone, prolactin, TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone).
Example: Without pituitary signals, the thyroid and adrenal glands wouldn’t know when to release their hormones.
🧠 Hypothalamus – The Boss of the Pituitary
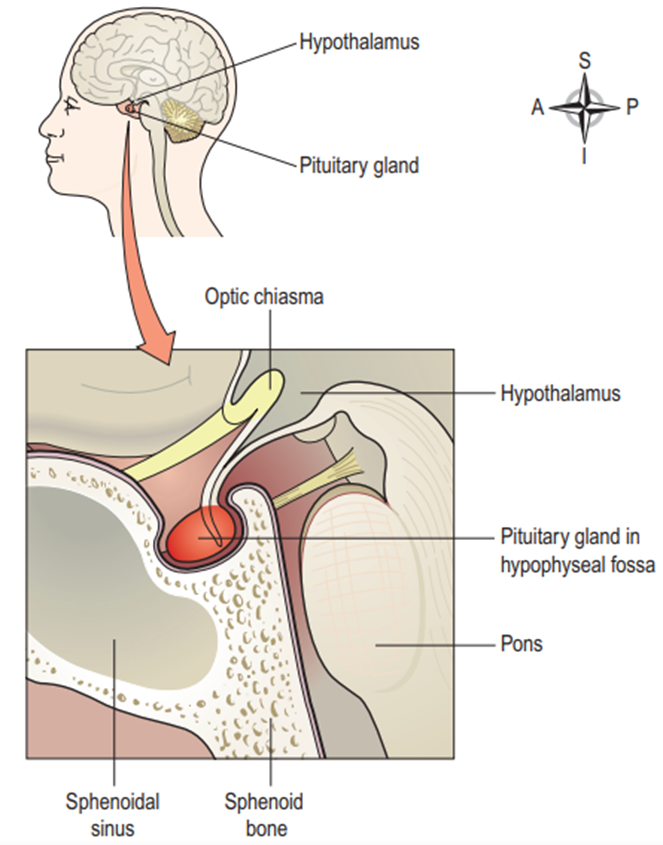
Location: Just above the pituitary.
Function: Connects the brain with the endocrine system.
Controls hunger, thirst, sleep, and body temperature.
🌙 Pineal Gland – The Body Clock
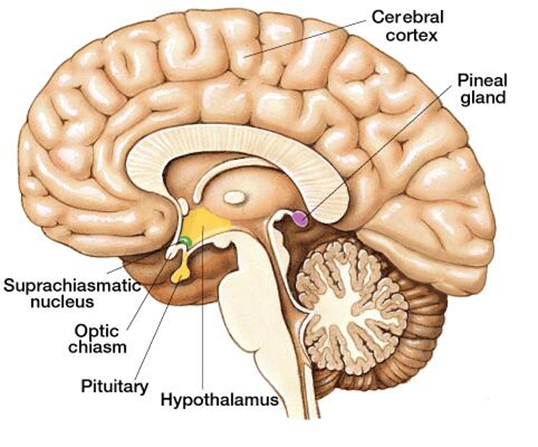
Location: Middle of the brain.
Hormone: Melatonin.
Function: Controls sleep-wake cycle.
Example: That sleepy feeling at night? Thank your pineal gland.
🦋 Thyroid Gland – The Energy Manager
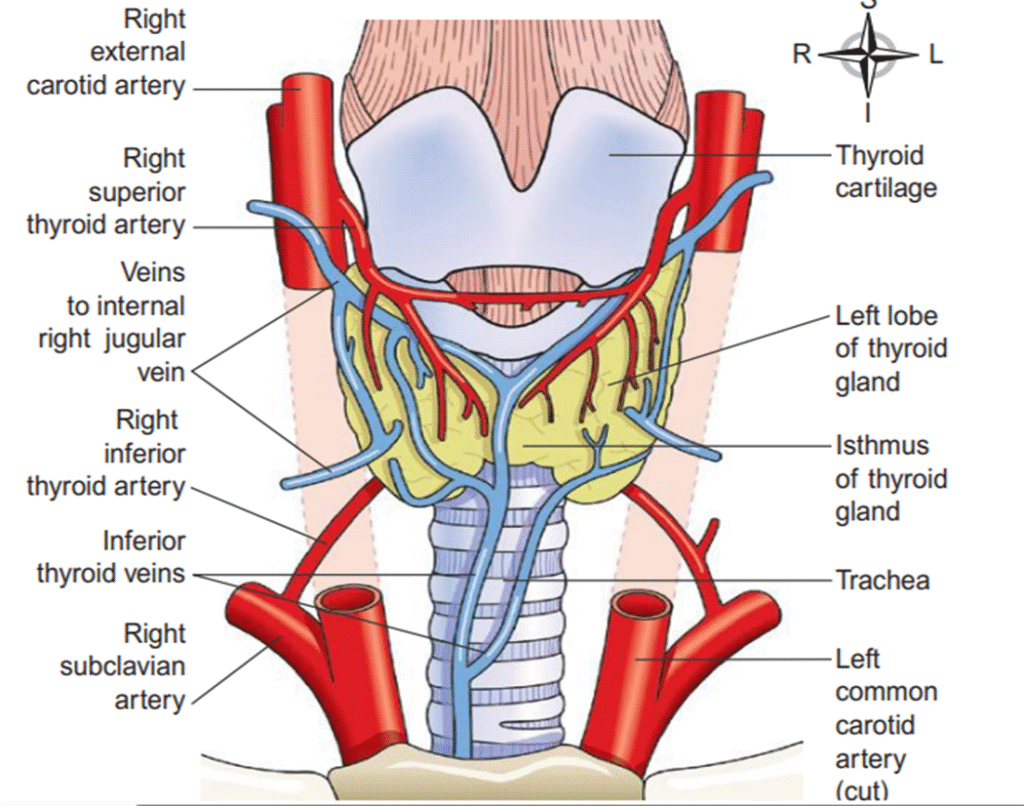
Location: Neck (front side).
Hormones: T3 (Triiodothyronine), T4 (Thyroxine).
Function: Controls metabolism (how fast body burns food for energy).
Common problem: Hypothyroidism (low thyroid activity) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
📍 Parathyroid Glands – The Calcium Balancers
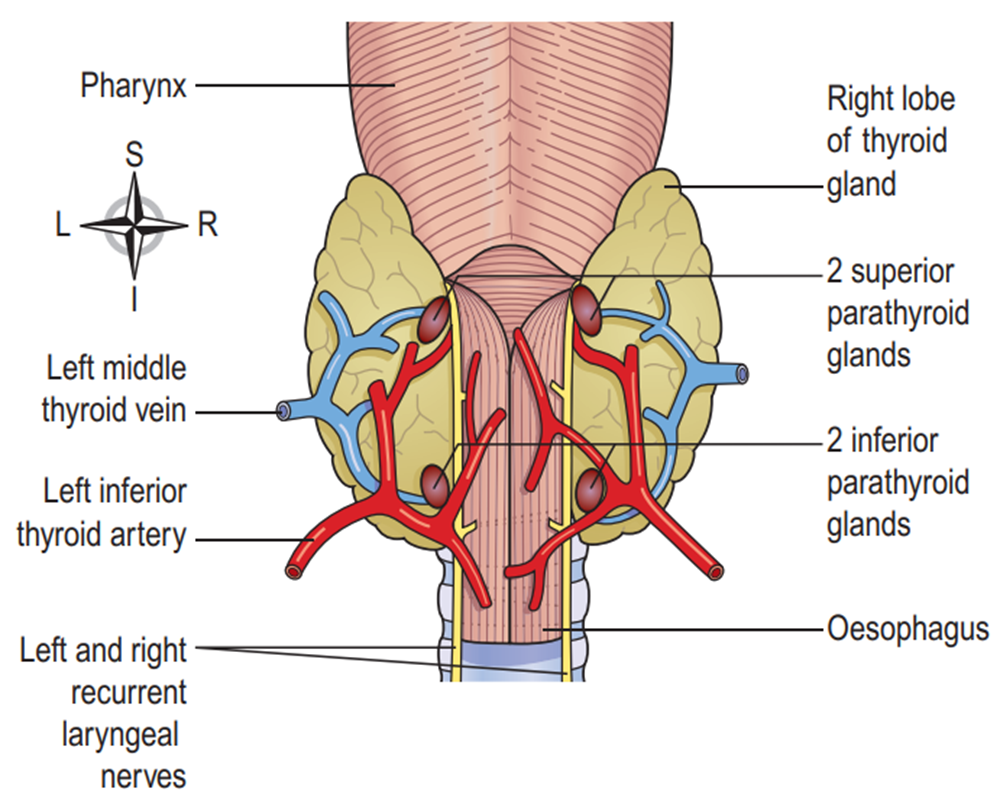
Location: Behind the thyroid (4 small glands).
Function: Maintain calcium levels in blood and bones.
⚡ Adrenal Glands – The Stress Fighters
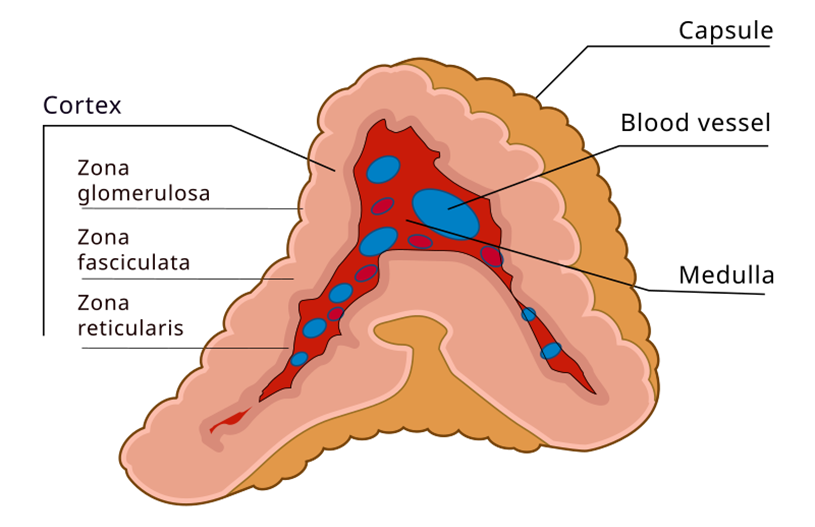
Location: On top of kidneys.
Hormones: Adrenaline, cortisol, aldosterone.
Function: Help body respond to stress, regulate blood pressure, salt balance.
🍬 Pancreas – The Blood Sugar Regulator
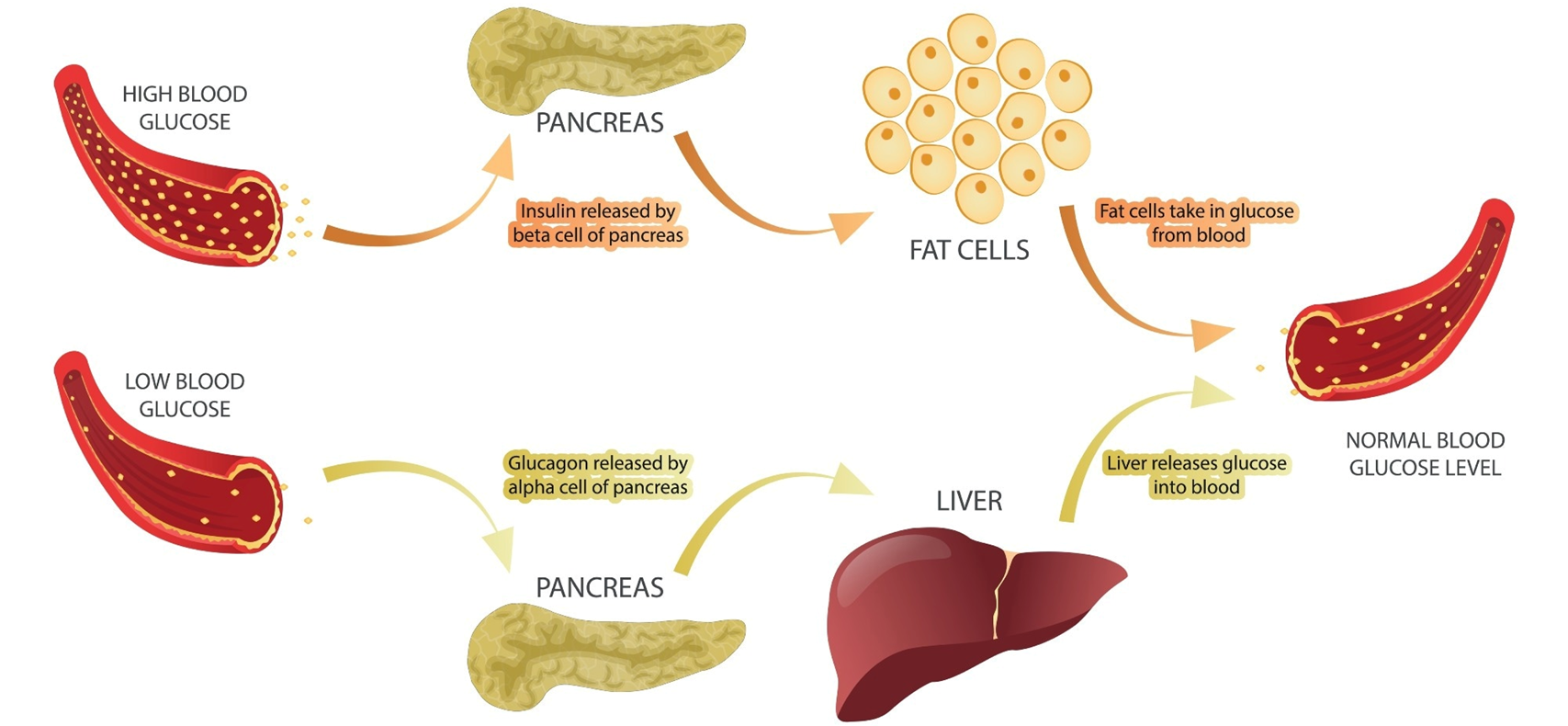
Location: Near stomach.
Hormones: Insulin, glucagon.
Function: Control blood sugar.
Disorder: Diabetes occurs when insulin is not working properly.
🌸 Ovaries (Females) – The Female Hormone Center
- Hormones: Estrogen, progesterone.
- Functions: Control menstrual cycle, pregnancy, female body changes.
- Disorder: PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) – very common in Indian women.
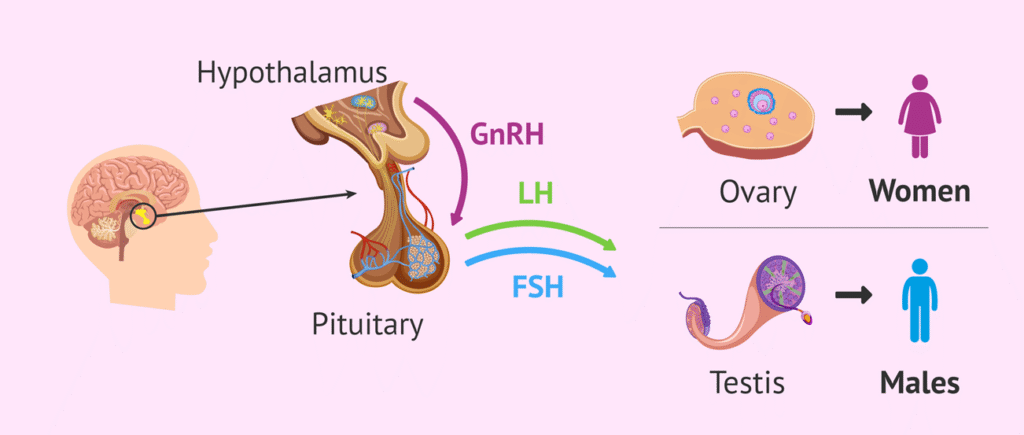
⚽ Testes (Males) – The Male Hormone Center
- Hormone: Testosterone.
- Function: Male puberty changes, sperm production, muscle strength.
Importance of Hormones in Daily Life
Hormones affect:
- Mood (happy, sad, stressed)
- Sleep quality
- Energy levels
- Body weight
- Growth and development
- Sexual health
- Fertility
- Skin health (pimples, glow, dryness)
👉 Even a small hormonal imbalance can affect health, which is why the endocrine system is so important.
Common Endocrine Disorders
1. Diabetes Mellitus
- Caused by lack of insulin or poor response to insulin.
- Very common in India (India is called the diabetes capital of the world).
- Symptoms: Excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue.
2. Thyroid Disorders
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
- Goiter (swelling of thyroid).
3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Hormonal imbalance in women.
- Symptoms: Irregular periods, facial hair, weight gain.
- Increasing rapidly in young Indian women.
4. Growth Disorders
- Too much growth hormone → Gigantism.
- Too little growth hormone → Short stature.
5. Adrenal Disorders
- High cortisol (Cushing’s syndrome).
- Low cortisol (Addison’s disease).
How Lifestyle Affects the Endocrine System
Our daily habits directly affect our hormonal balance.
- Poor diet → obesity, diabetes, thyroid problems.
- Stress → high cortisol, anxiety.
- Lack of sleep → disturbed melatonin, weight gain.
- Pollution & chemicals → disrupt hormones (endocrine disruptors).
Modern lifestyle, especially in cities of India, adds extra challenges. Long working hours, junk food, less physical activity, and exposure to plastics and chemicals disturb hormonal health.
Natural Ways to Keep Hormones Balanced
- Eat a balanced diet (whole grains, fruits, vegetables, proteins).
- Exercise regularly (yoga, walking, gym).
- Sleep 7–8 hours.
- Manage stress (meditation, hobbies).
- Avoid junk food and excessive sugar.
- Stay hydrated.
In Indian tradition, practices like yoga, pranayama, and Ayurveda herbs (ashwagandha, shatavari, giloy) are also linked to better hormonal balance. Globally too, mindfulness and natural diets are encouraged.
Endocrine System Across Ages
- Children: Growth and puberty. Hormones decide height, bone strength, and teenage changes.
- Adults: Energy, reproduction, stress management. Balanced hormones are needed for fertility and mental health.
- Elderly: Slower metabolism, menopause in women, lower testosterone in men. Hormones influence aging, bone health, and memory.
Future of Endocrine Health
Science and technology are rapidly advancing. Some upcoming developments include:
- AI-based diagnosis of diabetes and thyroid problems.
- New medicines for PCOS and infertility.
- Gene therapy for hormonal disorders.
- Increased awareness in India about lifestyle and endocrine health.
This future looks promising, but prevention and awareness will always remain the first step.
Conclusion
The endocrine system is one of the most fascinating and essential systems of the human body. It silently controls our growth, emotions, metabolism, reproduction, and overall health. Sadly, modern lifestyle, stress, and poor diet are disturbing hormonal balance for millions worldwide, especially in India.
The good news is – with awareness, healthy habits, and timely medical care, we can protect our endocrine system and lead a balanced life.
👉 Next time you feel tired, moody, or notice sudden weight changes, remember – your hormones might be trying to tell you something!
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on the Endocrine System
1. What is the endocrine system and why is it important?
The endocrine system is a network of glands in our body that release hormones. These hormones control many essential functions like growth, mood, sleep, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response. Without this system, our body would lose balance, and everyday processes like digestion, energy use, or fertility would not work properly. It is often called the body’s silent messenger system because it works quietly but influences almost everything.
2. How does the endocrine system work?
The endocrine system works by releasing hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones travel to specific target organs and give instructions. For example, when blood sugar rises, the pancreas releases insulin to bring it back to normal. Unlike the nervous system, which acts very fast, the endocrine system works slowly but has long-lasting effects.
3. What are the major glands of the endocrine system?
The main endocrine glands are:
- Pituitary gland – the “master gland” controlling others.
- Hypothalamus – connects brain and hormones.
- Pineal gland – regulates sleep.
- Thyroid gland – controls metabolism and energy.
- Parathyroid glands – maintain calcium balance.
- Adrenal glands – help with stress response.
- Pancreas – regulates blood sugar.
- Ovaries (in females) – produce estrogen and progesterone.
- Testes (in males) – produce testosterone.
4. What is the difference between the endocrine system and the nervous system?
The nervous system uses electrical signals to send quick, short messages (like touching something hot and pulling your hand away). The endocrine system uses hormones that travel in the blood. These act more slowly but their effects last longer (like growth, puberty, or metabolism). Both systems work together to maintain body balance.
5. What are common endocrine disorders?
Some common problems linked to the endocrine system include:
- Diabetes – due to problems with insulin from the pancreas.
- Thyroid disorders – hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and goiter.
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) – common in women, causes irregular periods and hormonal imbalance.
- Growth disorders – too much or too little growth hormone.
- Adrenal issues – like Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease.
6. Why are thyroid problems so common in India?
Thyroid problems are very common in India due to a mix of lifestyle, diet, and genetics. Earlier, iodine deficiency was a major cause, but now stress, poor diet, pollution, and sedentary lifestyle also play a role. Hypothyroidism (low thyroid function) is especially common in Indian women.
7. Can lifestyle affect hormonal balance?
Yes, lifestyle has a huge impact on hormones. Poor diet, lack of sleep, stress, and pollution can disturb the endocrine system. For example, eating too much junk food can cause obesity and diabetes. Stress can increase cortisol, leading to anxiety and weight gain. Good habits like balanced diet, exercise, yoga, and proper sleep help keep hormones healthy.
8. How can we keep our endocrine system healthy naturally?
To keep your hormones balanced, you can:
- Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins.
- Avoid excess sugar and junk food.
- Exercise regularly – even yoga and walking help.
- Get 7–8 hours of proper sleep.
- Manage stress through meditation, hobbies, or deep breathing.
- Stay hydrated and avoid harmful chemicals in plastics and cosmetics.
9. What role does the endocrine system play in puberty?
Puberty is a period of body changes during teenage years, and hormones control it completely. In boys, testosterone leads to deeper voice, muscle growth, and facial hair. In girls, estrogen and progesterone cause menstruation, breast development, and other female changes. These changes are guided by signals from the pituitary gland to the testes or ovaries.
10. What is the future of endocrine health?
The future looks promising. With AI-based diagnosis, doctors can detect diabetes and thyroid problems faster. New treatments for PCOS, infertility, and hormonal imbalances are being developed. People are becoming more aware of lifestyle’s impact on hormones. Globally and in India, there is more focus on prevention through diet, exercise, yoga, and holistic health practices.
More Post
